The sar command collect, report, or save UNIX / Linux system activity information. It will save selected counters in the operating system to the /var/log/sa/sadd file. Fromlinux-logo the collected data, you get lots of information about your server:
- CPU utilization
- Memory paging and its utilization
- Network I/O, and transfer statistics
- Process creation activity
- All block devices activity
- Interrupts/sec etc.
commands explain
sar : Displays the data.
sa1 and sa2: Collect and store the data for later analysis. The sa2 shell script write a daily report in the /var/log/sa directory. The sa1 shell script collect and store binary data in the system activity daily data file.
sadc – System activity data collector. You can configure various options by modifying sa1 and sa2 scripts. They are located at the following location:
/usr/lib64/sa/sa1 (64bit) or /usr/lib/sa/sa1 (32bit) – This calls sadc to log reports to/var/log/sa/sadX format.the sar comand a a prt of this tool sysstat, to install it
Sar is apart of sysstat tool, you can install it using the following command :
yum install syssstat
Now make this modification to generate a file every 10 minutes
#vim /etc/cron.d/sysstat */10 * * * * root /usr/lib/sa/sa1 -I -d 1 1 # generate a daily summary of process accounting at 23:53 53 23 * * * root /usr/lib/sa/sa2 -A
# vi /etc/sysconfig/sysstat # sysstat-10.1.5 configuration file. # How long to keep log files (in days). # If value is greater than 28, then log files are kept in # multiple directories, one for each month. HISTORY=28 # Compress (using gzip or bzip2) sa and sar files older than (in days): COMPRESSAFTER=31 # Parameters for the system activity data collector (see sadc manual page) # which are used for the generation of log files. # *note SADC_OPTIONS="-S DISK" # *note : valid options INT ⇒ System Interrupts DISK ⇒ Block Devices SNMP ⇒ SNMP statistics IPV6 ⇒ IPv6 statistics POWER ⇒ Power Management statistics ALL ⇒ All of the above XDISK ⇒ DISK + Partition statistics XALL ⇒ All of the above (ALL + XDISK)
Option Description
-u : CPU utilization statistics
-r : Memory utilization statistics
-b :I/O and transfer rate statistics
-B : Paging statistics
-d : Activity for each block device
-n : [keyword] Network statistics
-q : Queue length and load averages
-A : Display All
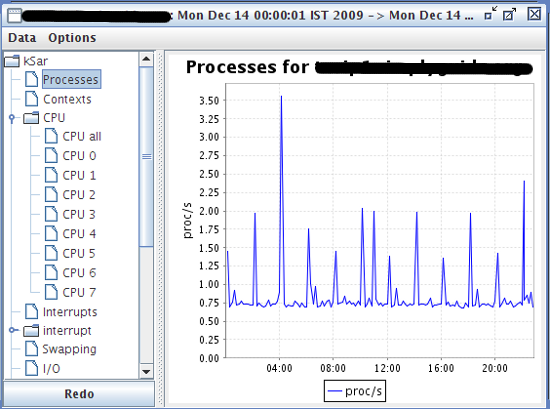
How Do I Generate sar Graphs Using kSar?
First, Download kSar grapher tool
you need to grab sar command statistics from the server named server1. Type the following command to get stats, run:
[server1 ]# LC_ALL=C sar -A sa08 > /tmp/sar.data.txt [server1 ]# LC_TIME="POSIX" sar -A -f sa08 > /tmp/sar.data.txt
Switch to kSar Windows. Click on Data > Load data from text file > Select sar.data.txt from /tmp/ > Click the Open button.
Now, the graph type tree is deployed in left pane and a graph has been selected:
![]()